1 chemical linking via covalent bonds 2 coupling via recombinant fusion constructs. Vaccination is an efficient and cost-effective form of preventing infectious diseases.
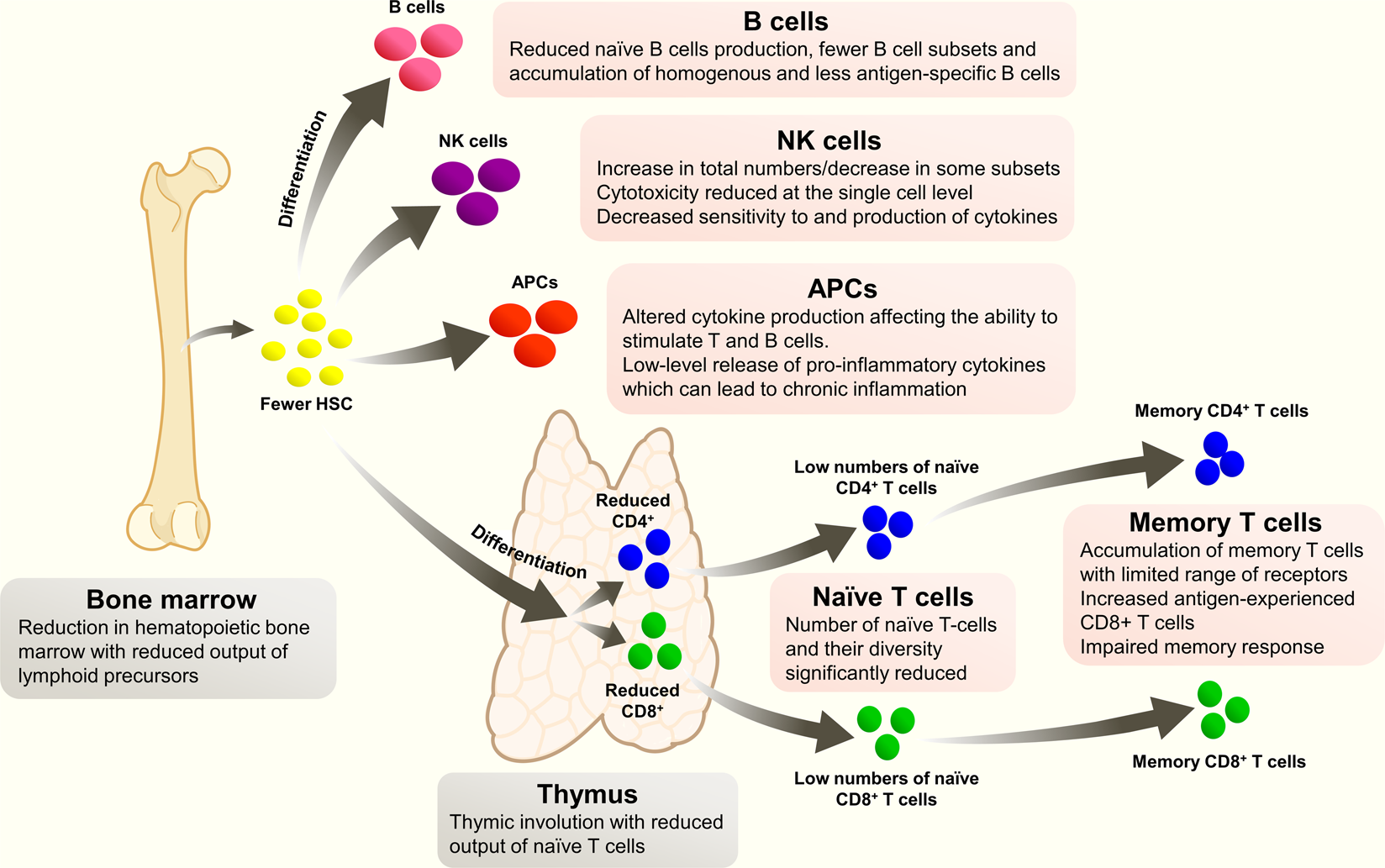
Vaccination As A Preventative Measure Contributing To Immune Fitness Npj Vaccines
The transdermal vaccine route offers an opportunity to improve vaccine administration.
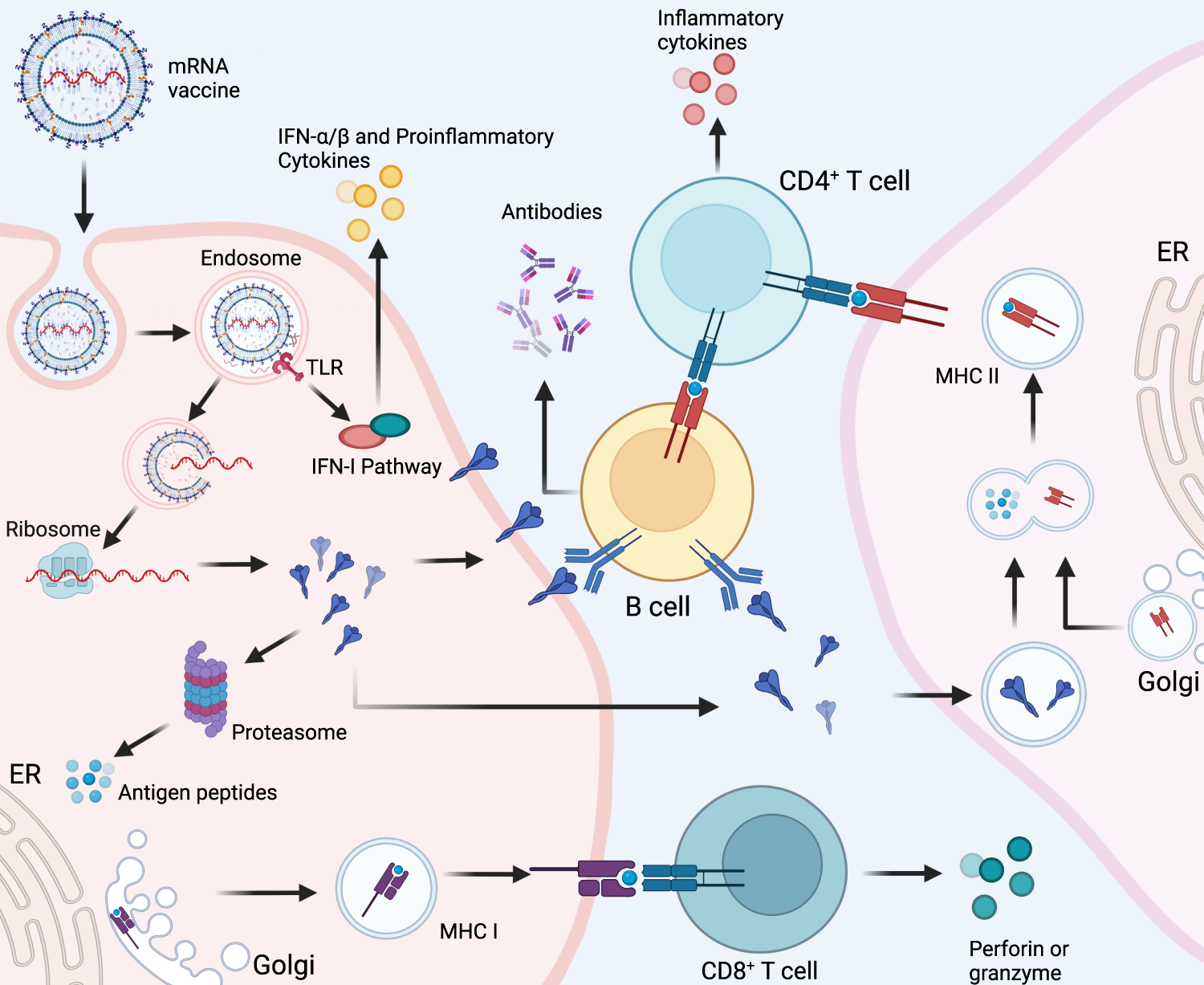
. A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe its toxins or one of its surface proteinsThe agent stimulates the bodys immune system to recognize the agent. One of the challenges to creating RNA vaccines is making sure that the RNA gets into the right immune cells and produces enough of the encoded protein. Liang says We summarize the development of preclinical therapeutic cancer vaccines and the advancements of nanomaterial-based delivery.
Articles for the review study were. Optimized delivery can also enhance the immune response or effector presentation biocompatibility and biosafety Susanne et al 2018. In particular they describe novel polymeric.
However most currently available vaccines are. Solid particulate systems such as microspheres and lipospheres are being exploited for vaccine delivery Table 1 based on the fact that intestine is an imperfect barrier to small particulates. The impact of the ongoing pandemic of coronavirus 2019 on immunisation campaigns in low- and middle-income countries is concerning.
New emphasis on and requirements for demonstrating health care quality have increased the need for evidence-based methods to disseminate practice guidelines. It is therefore essential to find suitable delivery methods for mRNA vaccines to maximize the immunogenic window while minimizing any vaccine-associated risks. A review of the recent advances.
Considerations for school- and non-school based immunization program. Food and Drug Administration and similar authorities around the world. Using cationic microparticles as a delivery system for DNA vaccines resulted in significantly enhanced immune responses in comparison with immunization using naked DNA in mice 39 and in non-human.
The preprint of the study. With regard to impact on pediatric immunization coverage we aimed to compare a financial incentive program pay-for-performance P4P and a virtual quality improvement technical. This review highlights the potential role of skin as a vaccine delivery route using a microneedle system examines recent advancements in microneedle fabrication techniques and provides an update on potential preclinical and clinical studies on vaccine delivery through microneedle systems against various infectious diseases.
Further detailing what the review has achieved Dr. When designing the best delivery system for a vaccine a lot can. In this Special Focus experts in the field describe recent innovations in the design evaluation and use of novel vaccine delivery devices and systems.
Vaccine delivery systems can be classified as follows. In this review we provide an overview of the current vaccine platforms adjuvants and delivery systems that are currently being investigated or have been approved. As the pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 COVID-19 continues to thread its way around the globe disruptions are occurring in healthcare commerce.
Antigens entrapped in such particulates when taken up by M-cells can generate immunity. Examples of vaccine delivery systems include liposomes emulsions and. Article PubMed Google Scholar JCVI statement on the annual influenza vaccination programme extension of the programme to children.
Additionally the vaccine must stimulate a strong enough response that the immune system can wipe out the relevant bacteria viruses or cancer cells when they are subsequently encountered. 11 In this article we review the. Scientists have developed an inhalation delivery system for vaccines that generates potent immune responses in mice and non-human primates without causing lung damage an advance that may lead to.
Vaccines based on messenger RNA mRNA are attracting worldwide attention as the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines have been authorized for emergency use by the US. A reliable and safe vaccine delivery system. This is the first time that mRNA-based vaccines have ever been approved for use on healthy population 1 and marks a critical.
Literature review of HPV vaccine delivery strategies. Concerted efforts by researchers on alternative vaccine delivery routes have yielded a range of novel delivery devices with potential to enhance immunogenicity and stability. This review introduces these studies based on their research emphasis on functional design or administration route optimization presents recent progress and discusses features of new vaccine delivery systems providing.
According to the World Health Organization vaccine development and mass immunization strategies remain critical initiatives especially because of the continued threat. Drug delivery system DDS is a generic term for a series of physicochemical technologies that can control delivery and release of pharmacologically active substances into cells tissues and organs such that these active substances could exert optimal effects 1 2In other words DDS covers the routes of administration and drug formulations that efficiently. Liposomes as vaccine delivery systems.
A vaccine delivery system is the means by which the immune-stimulating agent constituting the vaccine is packaged and administered into the human body to ensure that the vaccine reaches the desired tissue. The preprint described Modernas coronavirus vaccine candidate as using delivery technology that appears to be covered in the Arbutus patent that was upheld last week. There has been an increase in state-level rates of nonmedical exemptions from immunization requirements.
A Review of Transdermal Vaccine Delivery. Paul P Fabio A. But the successful utilization of this system for vaccine drug delivery mainly depends on design of device to facilitate microneedle infusion vaccine stability and storage in system recovery of skin on removal of microneedle and improved patient compliance.
In this Review we discuss the approaches currently being used to optimize the delivery of antigens and enhance vaccine efficacy. Background Immunization supply chains iSCs move vaccines from manufacturer to point of use with the added complexities of requiring cold chain and an increasing need for agility and efficiency to ensure vaccine quality and availability. There are two methods for designing CPP incorporating immunogenic antigens.
Therefore vaccine delivery systems may significantly affect the final outcome of genetic and other novel vaccines and are vital for their development. Two applications of CPP already validated in vaccine studies are delivery of tumor-associated antigens into antigen-presenting cells APCs and use as a non-viral gene delivery vehicle in DNA vaccines. This review compiles the key delivery system technologies currently available for.
A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease. With the advent of immune checkpoint inhibitors we also review the potential of these to be used with cancer vaccines to improve efficacy and help to overcome the immune suppressive tumor. COVID-19 disrupts vaccine delivery.
Parry BVSc MRCVS MSc DipACVP. Underperforming iSCs have been widely acknowledged as a key constraint to achieving high immunization coverage rates in low-.
Covid 19 Vaccine Brand Hesitancy And Other Challenges To Vaccination In The Philippines Plos Global Public Health
Covid 19 Vaccine Brand Hesitancy And Other Challenges To Vaccination In The Philippines Plos Global Public Health
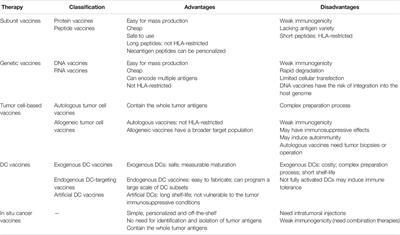
Frontiers Hitchhiking On Controlled Release Drug Delivery Systems Opportunities And Challenges For Cancer Vaccines Pharmacology
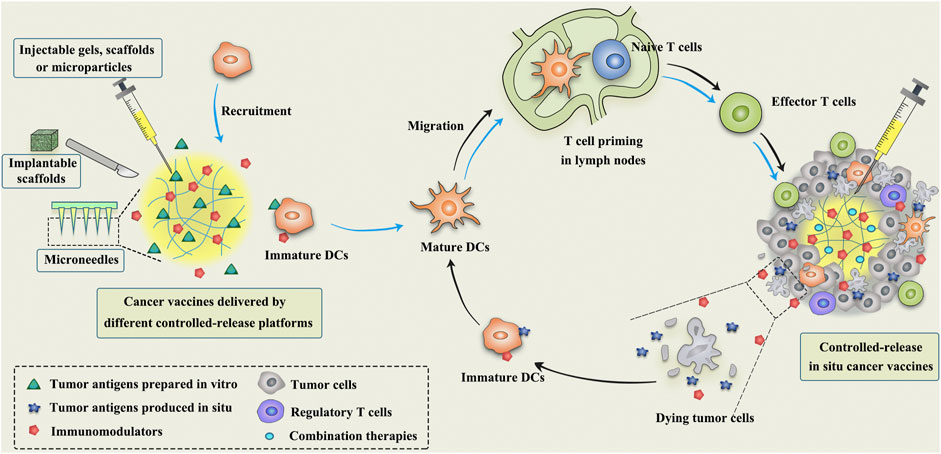
Frontiers Hitchhiking On Controlled Release Drug Delivery Systems Opportunities And Challenges For Cancer Vaccines Pharmacology
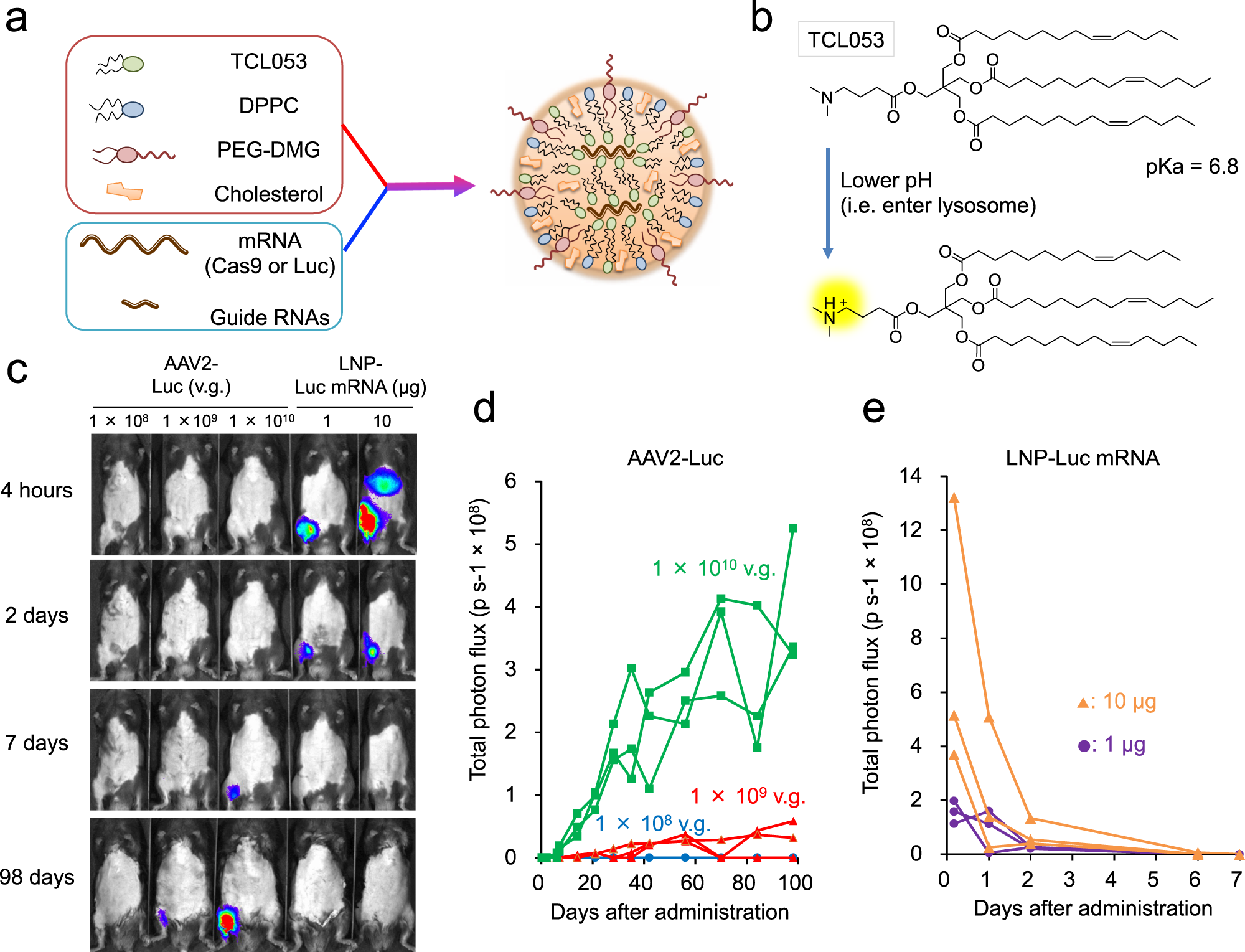
Low Immunogenicity Of Lnp Allows Repeated Administrations Of Crispr Cas9 Mrna Into Skeletal Muscle In Mice Nature Communications

Advances In Covid 19 Mrna Vaccine Development Signal Transduction And Targeted Therapy
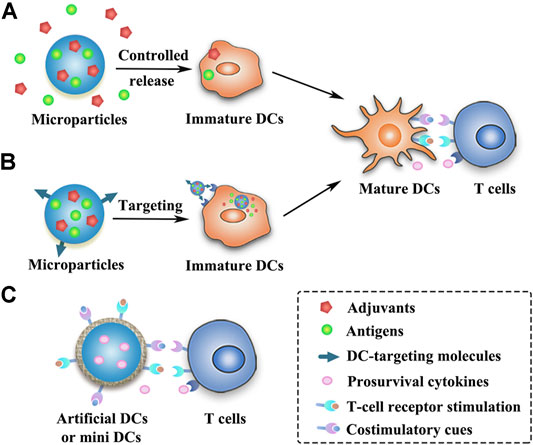
Frontiers Hitchhiking On Controlled Release Drug Delivery Systems Opportunities And Challenges For Cancer Vaccines Pharmacology
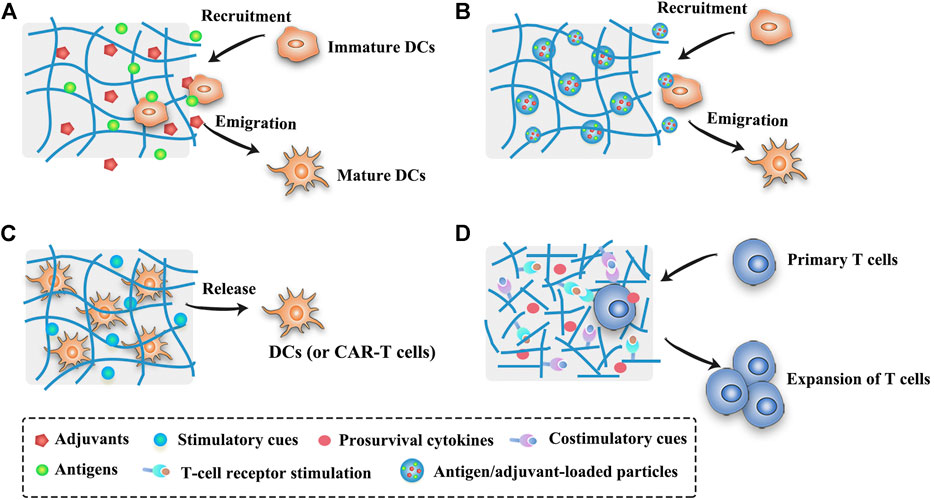
Frontiers Hitchhiking On Controlled Release Drug Delivery Systems Opportunities And Challenges For Cancer Vaccines Pharmacology

Optimization Of Lipid Nanoparticles For Intramuscular Administration Of Mrna Vaccines Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids

Intranasal Covid 19 Vaccines From Bench To Bed Ebiomedicine
Covid 19 Vaccine Brand Hesitancy And Other Challenges To Vaccination In The Philippines Plos Global Public Health

Intranasal Covid 19 Vaccines From Bench To Bed Ebiomedicine
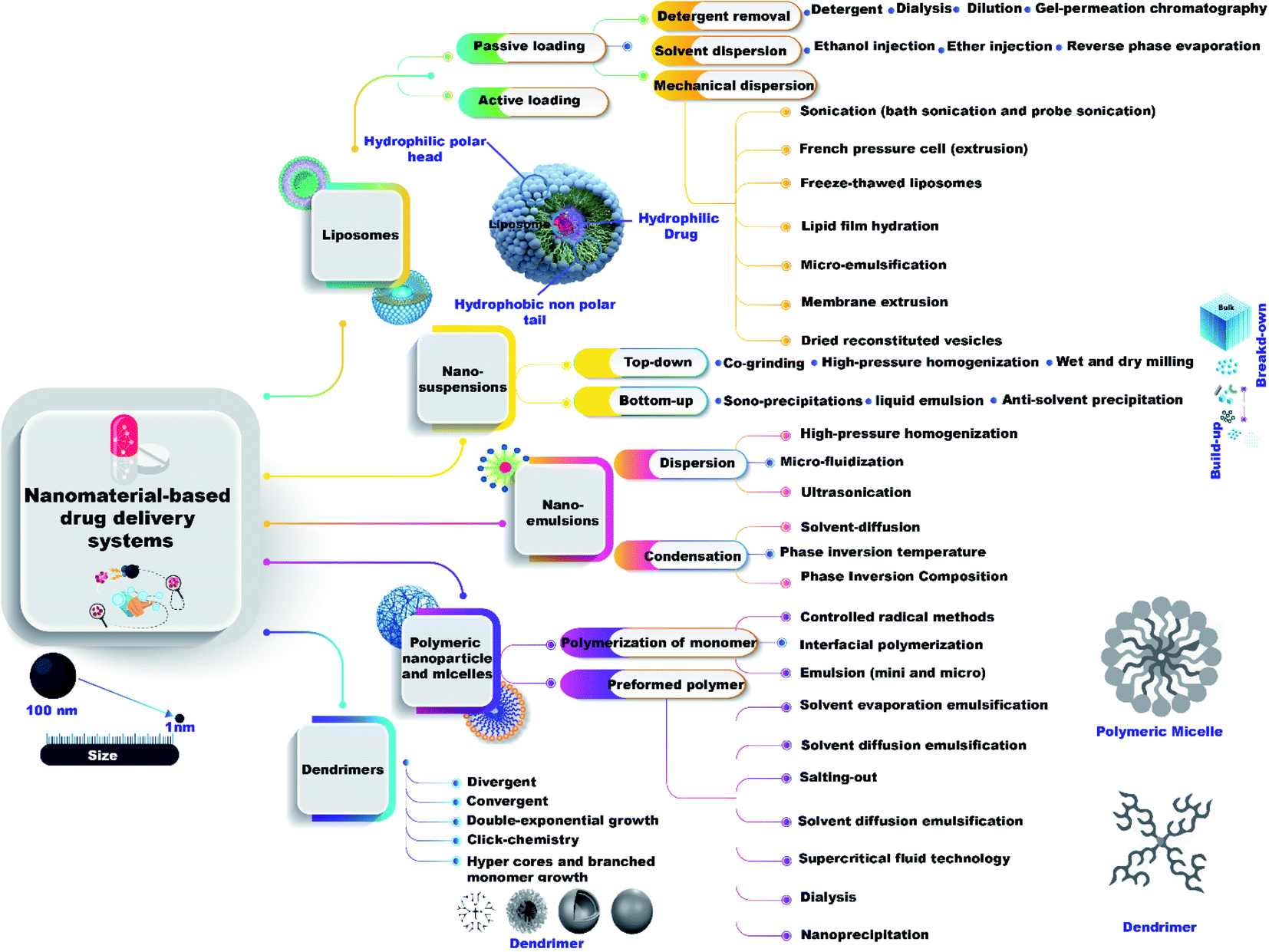
Nanomaterial Based Drug Delivery Systems As Promising Carriers For Patients With Covid 19 Rsc Advances Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 D1ra04835j

Intranasal Covid 19 Vaccines From Bench To Bed Ebiomedicine
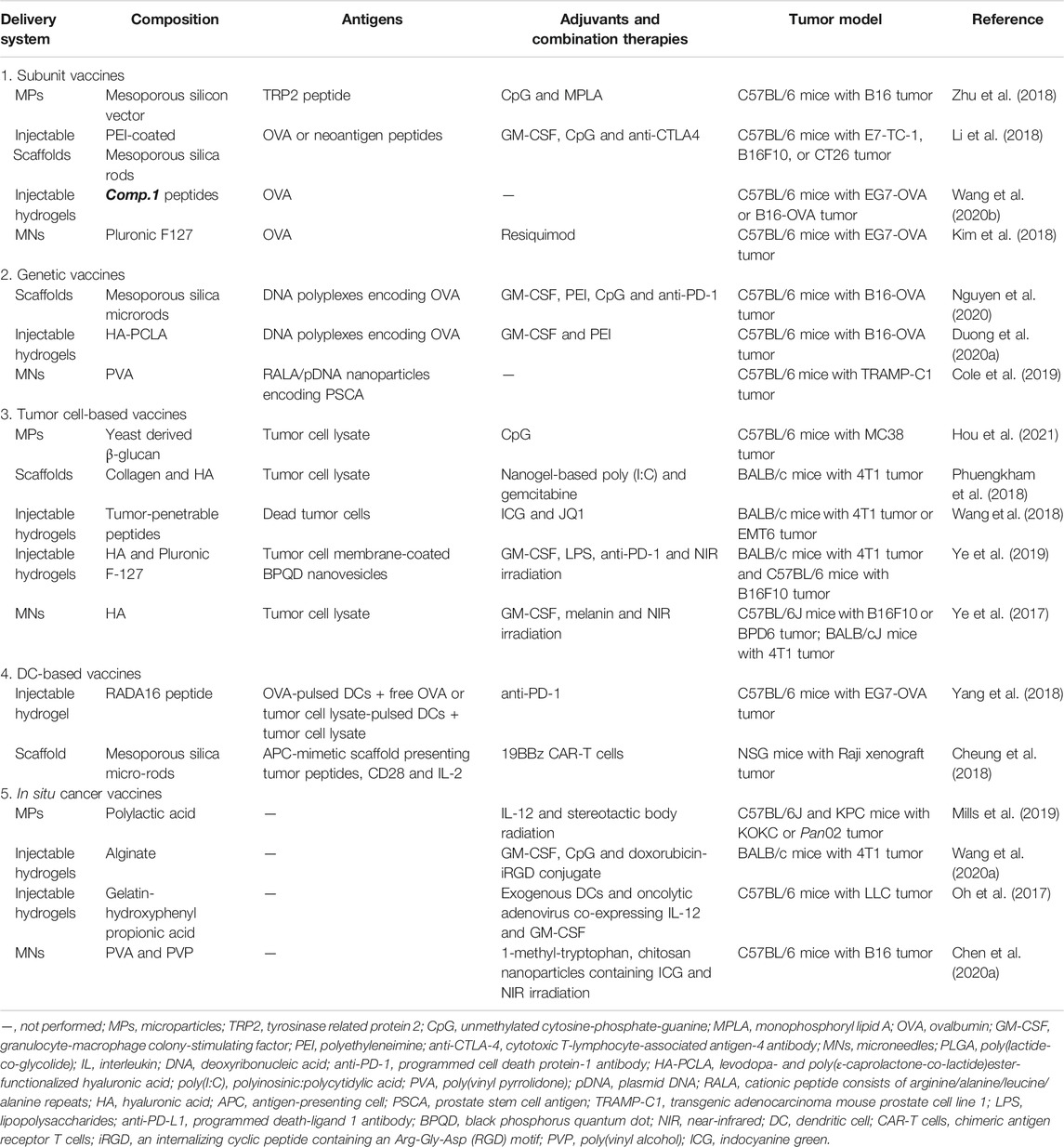
Frontiers Hitchhiking On Controlled Release Drug Delivery Systems Opportunities And Challenges For Cancer Vaccines Pharmacology
Vaccines February 2022 Browse Articles

Mrna Therapeutics Beyond Vaccine Applications Trends In Molecular Medicine
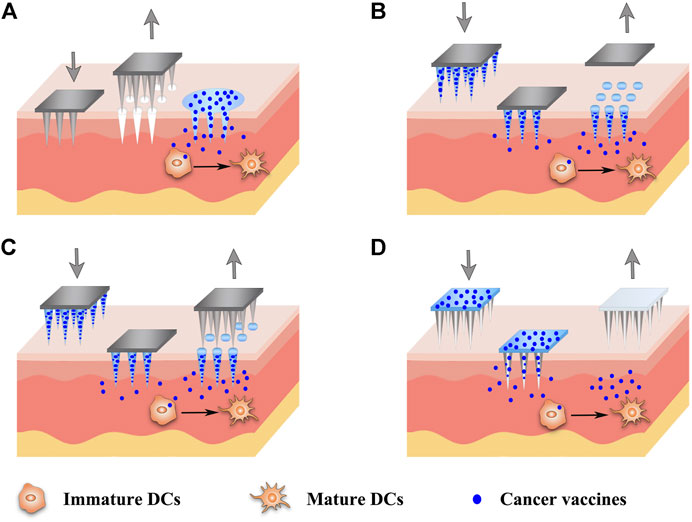
Frontiers Hitchhiking On Controlled Release Drug Delivery Systems Opportunities And Challenges For Cancer Vaccines Pharmacology
